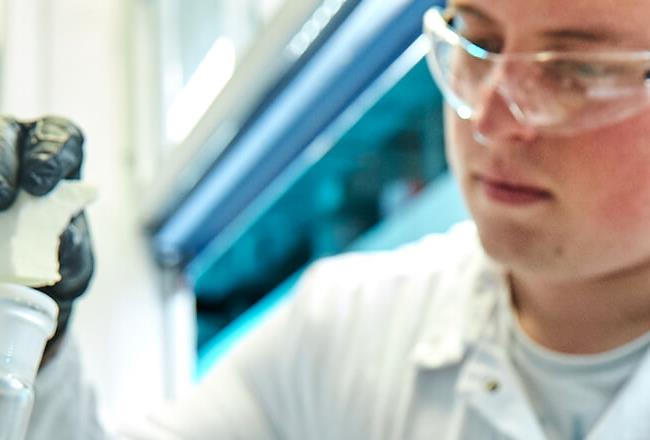
Innovative Recycling – More Reuse, Less Plastic Waste
Plastics are the material of our time. They help us cope with global challenges, such as aligning economy and society with climate-neutrality. But they also provide solutions for new mobility concepts, accelerate the transition to green energy and make our cities more livable.
But to achieve a truly sustainable future and permanently protect the environment, our attitude towards consumption and waste must change in our widespread throw-away society. For decades, mankind has lived far beyond its means and now consumes the natural resources of 1.7 Earths.
Most consumer products end up as waste. By 2050, the annual amount worldwide is expected to rise by 70 percent. Already a third of the world’s municipal waste – around two billion tons per year – is not properly disposed of. Each year, 22 million tons of plastic waste alone ends up in the oceans and in the environment. On the other hand, the plastic recycling rate is still low: worldwide, just 9 percent of all plastic waste is recycled.
Covestro Promotes Recycling
One thing is clear: more old plastics must be used as a raw materials source. The industry is strongly in favor of this. For example, it wants to help achieve the European Union target of using ten million tons of recycled plastics per year by 2025. Plastics manufacturers also intend to invest eight billion euros into chemical recycling by 2030. And in the USA, for example, all plastic packaging must be completely reused or recycled by 2030. According to a study, almost 60 percent of plastic production could be based on recycling by the middle of the century.
As an industrial pioneer of the Circular Economy, Covestro wants to promote plastic recycling. In particular, the company aims to develop innovative technologies and make them marketable as quickly as possible. To this end, more than 20 research and development projects have been set up. Covestro is pursuing a broad technological approach to meet the wide range of products and markets.
When developing new plastic recycling paths, the material producer pays particular attention to energy efficiency. The new technologies should help reduce the carbon footprint of production processes and products and thus contribute to climate and environmental protection. At the same time, Covestro is working with customers and partners in the value chain to develop circular business models.
Chemical Recycling
Chemical recycling, which is still in its early stages, is particularly promising. Covestro sees great potential here. After all, for certain plastics it is the only possible method of industrial recycling. Chemical recycling is primarily relevant for products that are not recyclable or can only be mechanically recycled with great effort – if they are heavily contaminated or are made of several types of plastic which are difficult to separate.
Covestro is working intensively with partners to further develop chemical recycling and establish it on the market. The Europe-wide “Circular Foam” research project, which involves 23 different partners from nine countries and is coordinated by Covestro, could play an important role here. The goal is to use chemical processes on rigid polyurethane foam, which is used as an insulating material in refrigerators and buildings. These processes break the foam down into its molecules, which are then recomposed. This lighthouse project could save one million metric tons of waste, around three million metric tons of CO₂ emissions and 150 million euros in incineration costs every year in Europe from 2040.
Covestro has also developed a platform technology called Evocycle® CQ for recycling polyurethane foam – initially, it will be used for mattress soft foam components, which are recovered through chemical recycling.
There are three types of approaches to chemical recycling that Covestro is pursuing:
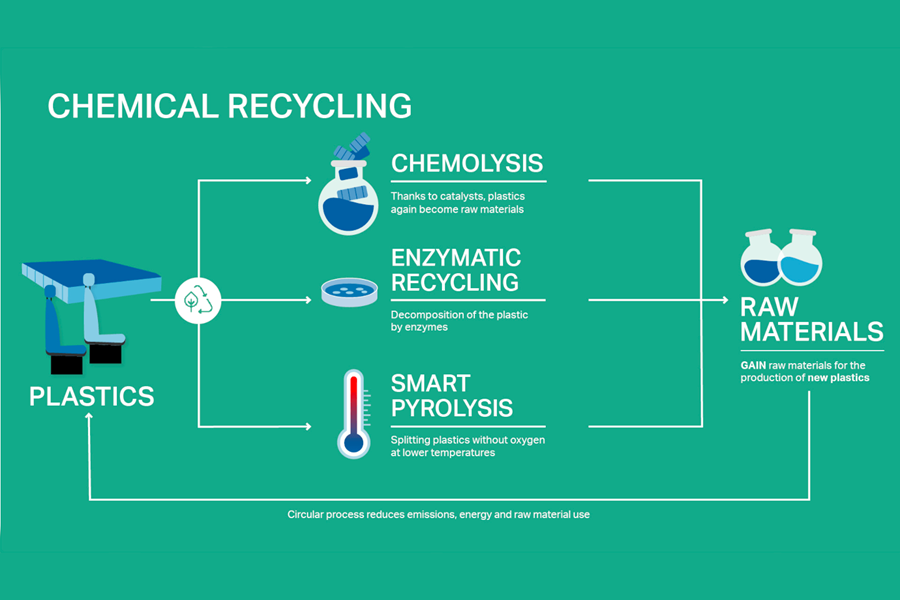
Here you can see CEO Markus Steilemann explaining the three types of chemical recycling at Covestro.
Mechanical Recycling
In mechanical recycling, waste materials are recycled into new raw materials without changing the base structure of the material. For example, after sorting and processing, plastic is crushed into granulate. This can be melted down and made into new plastic. One of the ways Covestro uses mechanical recycling is to transform used water bottles into high-grade plastic components for electronic and household appliances.
Together with partners, the company has also launched a pilot program in China to create circulation routes for high-grade plastics from old cars. For example, plastic granulate will be obtained from worn-out headlights and then reused for interior and exterior applications in vehicles. Partners on the German side include the car manufacturer Volkswagen, the testing organization TÜV Rheinland and the German Society for International Cooperation (GIZ), as well as the electric car manufacturer Nio and plastics recycler GEM from China.
Design for Recycling
It is important to design plastics so that they can be recycled in an optimal way at the end of their life and thus protect the environment. Covestro is actively working on this. For example, the company has created a guide to circular design together with the consulting firm Renato. It is intended to help manufacturers design plastic-based electric and electronic products and household devices that comply with a circular economy model.